Cmk
Machine Capability Index
Cmk (and Cm) are two denotations that represent machine capability. Cmk represents a very short term reflection of machine performance in relation to the tolerance limits (or specification limits).
Higher values for Cm and Cmk represent better machine performance.
Cm and Cmk describes machine capability using 20-50 consecutive measurements.
This is considered a very short term index since this process of collecting these consecutive measurments can NOT include stoppages, operator changes, tool changes, machine changes, environment changes, oil changes, etc.
Recall as the Fishbone shows, there are six factors that are generally accepted that create variation:
1) Environment
2) Machine
3) Operator
4) Method
5) Material
6) Measurement
For Cmk and Cm, the ONLY factors of variation that are at play are Measurement and Machine. Hence the reason for the name being machine capability and not process capability.
And it is the job of the Black Belt to quantify the measurement system variation and verfiy a passing MSA. This validates that the measurement system variation is minimal as a % of the total variation.
It's possible that the machine capability is the same (or equal) to the process capability but very very unlikely. The machine capability is is very short sampling and the best performance value out Cp, and Pp.
Cp and Pp will never exceed Cm. Cm will almost always be greater than Cp and Pp.
The process capability index measurements of Cpk, Cp, Pp, and Ppk will include stoppages and some or all of the above six sources of variation.
Cm does NOT account for the position of the spread within the tolerance limits. That is where Cmk comes into play.
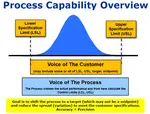
What does the Cm value mean?
The value of Cm is the number of times the spread of the machine's performance compared to the width of the tolerance.
To help understand Cm, if the Cm value is 2.0, that means the spread of the consecutive measurements will fit 2x into the tolerance width. The tolerance width is two as big as the data spread. The tolerance range is the range between the Lower Specification Limit (LSL) and the Upper Specification Limit (USL).
A Cm of 1.0 means the width of the data is equal to the width of the tolerances However, it does not indicate where the data is relateive to the tolerances In other words, if may not be centered at all and it could reside 100% outside of one of the tolerances.
So even if the spread of the data is not centered it is still the same width. Cm has no bearing of the position of its data relative to the specification (tolerances) limits or a target value (recall that target values may not always be the midpoint of the tolerances).
What does the "k" mean in Cmk
The addition of "k" in Cmk quantifies the amount of which a distribution is centered, in other words it accounts for shifting and location as it pertains to the tolerance or specifications. A perfectly centered process where the mean is the same as the midpoint will have a "k" value of 0.
The minimum value of "k" is 0 and the maximum is 1.0. A perfectly centered machine data spread will have Cm = Cmk.
Cmk, Cpk, and Ppk relate the standard deviation and centering of the process about the midpoint to the allowable tolerance specifications.
An estimate for Cmk = Cm(1-k).
and since the maximum value for k is 1.0, then the value for Cmk is always equal to or less than Cm.
Learn about these other Capability Indices
Search active Six Sigma job openings
Templates, Tables, and Calculators
Recent Articles
-
Process Capability Indices
Oct 18, 21 09:32 AM
Determing the process capability indices, Pp, Ppk, Cp, Cpk, Cpm -
Six Sigma Calculator, Statistics Tables, and Six Sigma Templates
Sep 14, 21 09:19 AM
Six Sigma Calculators, Statistics Tables, and Six Sigma Templates to make your job easier as a Six Sigma Project Manager -
Six Sigma Templates, Statistics Tables, and Six Sigma Calculators
Aug 16, 21 01:25 PM
Six Sigma Templates, Tables, and Calculators. MTBF, MTTR, A3, EOQ, 5S, 5 WHY, DPMO, FMEA, SIPOC, RTY, DMAIC Contract, OEE, Value Stream Map, Pugh Matrix

Site Membership
LEARN MORE
Six Sigma
Templates, Tables & Calculators
Six Sigma Slides
Green Belt Program (1,000+ Slides)
Basic Statistics
Cost of Quality
SPC
Control Charts
Process Mapping
Capability Studies
MSA
SIPOC
Cause & Effect Matrix
FMEA
Multivariate Analysis
Central Limit Theorem
Confidence Intervals
Hypothesis Testing
Normality
T Tests
1-Way ANOVA
Chi-Square
Correlation
Regression
Control Plan
Kaizen
MTBF and MTTR
Project Pitfalls
Error Proofing
Z Scores
OEE
Takt Time
Line Balancing
Yield Metrics
Sampling Methods
Data Classification
Practice Exam
... and more